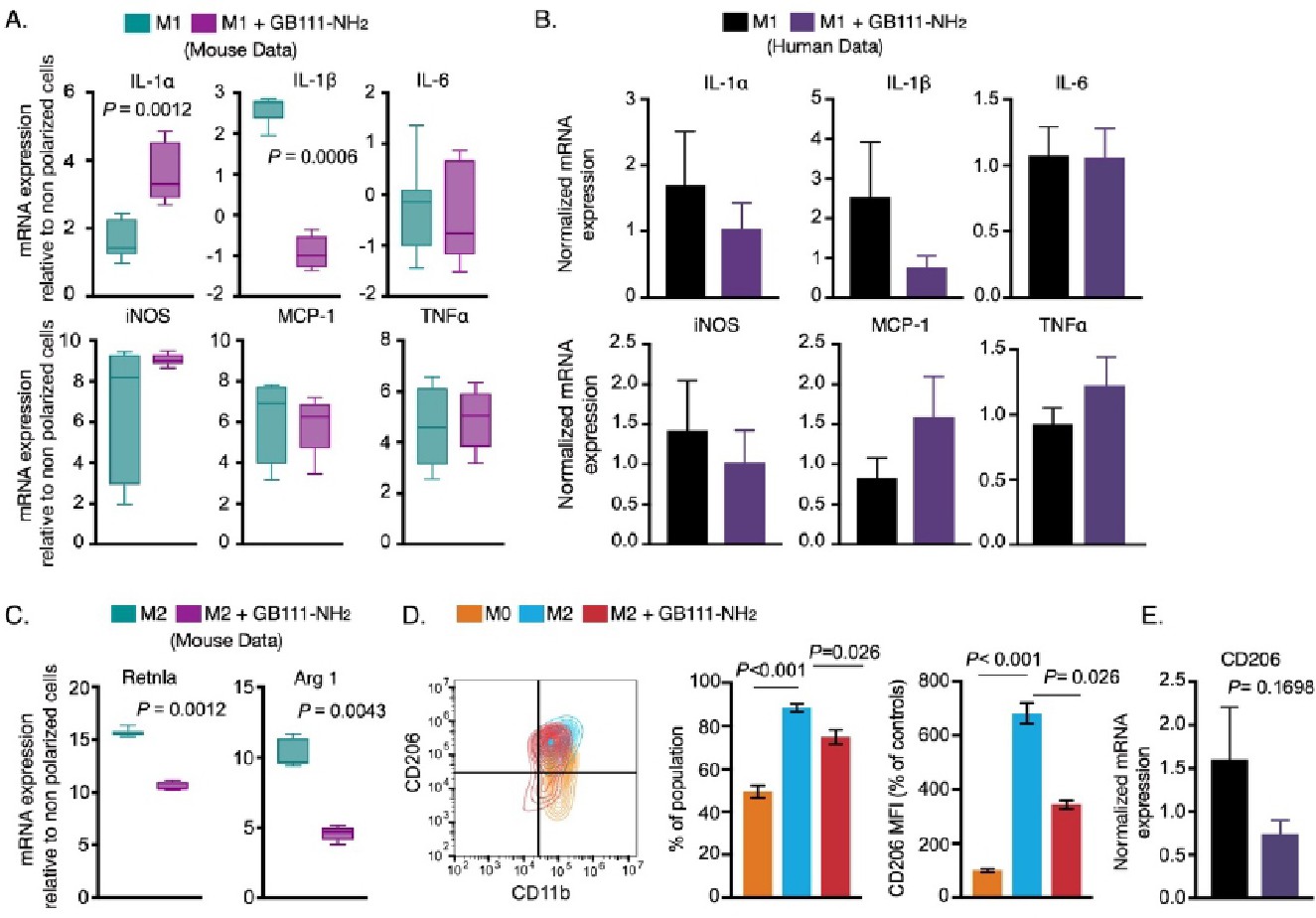
Fig. 7. Cathepsin dysfunction alters M2 phenotype. BMDMs were treated with GB111-NH2 or DMSO vehicle for 16 h and then polarized with LPS/INFγ (M1) or with IL-4 for 24 h (M2, anti-inflammatory). (A) Normalized expression of inflammatory cytokines in M1 BMDMs are presented relative to non-polarized BMDMs (6 biological replicates from three independent experiments). The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to evaluate statistical difference. (B) Human primary macrophages were pretreated with GB111-NH2 or DMSO control for 24 h and polarized to generate M1 phenotype with LPS/INFγ. Normalized expressions of inflammatory genes are presented in the bar graph. The data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=3 biological replicates). Student's t-test was used to evaluate statistical significance. (C) BMDMs were treated with GB111-NH2 for 16 h, then polarized to yield M2 phenotype in the presence of IL-4 for another 24 h. Normalized expressions of classical M2 markers, Retnla and ARG-1 are expressed as fold changes relative to non-polarized samples (n=6 biological replicates from three independent experiments). The Wilcoxon rank sum test was used to evaluate statistical differences between samples. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of CD206 expression in M2 polarized BMDMs. Contour plot showing CD11b and CD206 expression in M2 polarized BMDMs or in untreated cells with M0 as controls. CD206 positive cells were quantified from CD11b positive cells and presented as percentages of the population. The intensity of CD206 was analyzed relative to untreated BMDMs (M0) and presented as the percentage of untreated cells. The data are summarized over three biological replicates from two independent experiments. One-way ANOVA with Sidak's post hoc correction for multiple comparisons was used to evaluate statistical differences between groups. (E) mRNA expression of CD206 in human primary macrophages is shown in the bar graph (n=3 biological replicates). Two-tailed Student's t-test was used to evaluate statistical difference. Bar graphs present the mean ± SEM.